For the Dutch version, click here. They are two companies you don't often think about, but they are essential to your daily life. Every time you

In this digital era, keeping up with the rapidly changing economic environment is a time-consuming ordeal. One of the new ground-breaking technologies you have surely heard about is blockchain. Are you not sure what all this blockchain-talk is about and what changes it will bring when it is more widely integrated in our daily lives? Our editor Rob Donkers attempts to explain in understandable terms what blockchain is and how it could change the world. For some extra information or backstories, click on the endnotes that can be found throughout the article. Note that this is an attempt to introduce people to blockchain without making it too complicated. Blockchain is more than what is written down here, but the technical jargon was minimalized for the purpose of the article.
Fundamentals of Blockchain
Fundamentally, blockchain technology is a string of blocks, organized chronologically. Each of these blocks contain information about transactions that were made globally in a specific timeslot, often 10 minutes. It records all transactions that were made, and once a block of information is established, it is assumed that it is practically impossible to change. As long as a blockchain persists, all existing blocks are openly visible to everybody. This means that any amount of currency is traceable all the way back to its origin. There is no way to secretly transfer something, as all transactions appear in the blockchain, which is openly accessible. In order to keep a blockchain up and running, access to continuous computing power is a necessity. Transactions on a blockchain are not done with fiat currencies like Euros or Dollars. This is where blockchain currencies come in. Special currencies are used to enable transactions, named cryptocurrencies. Let’s take Bitcoin as example, as it is the most prevalent cryptocurrency at the moment. To do a transaction on the Bitcoin blockchain, Bitcoin has to be used. At the inception of the Bitcoin blockchain, a number of Bitcoins were distributed to enable payments. Unlike fiat currencies like Euros or Dollars, Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies can not be created out of thin air. Instead, a fixed amount of Bitcoin is released over time . After the initial release of Bitcoin, the only way the total amount of Bitcoins in circulation can be increased is by mining new Bitcoins. Simplified, an amount of Bitcoin is rewarded for the act of creating a new block on the blockchain. To choose who gets to create the new block, a digital puzzle has to be solved which takes a lot of computing power . The difficulty of this puzzle is updated regularly, so that on average one computer is chosen to write a new block every 10 minutes. Participating in this is called mining. This incentivizes people to contribute computing-power to the Bitcoin blockchain as long as the currency Bitcoin holds value .
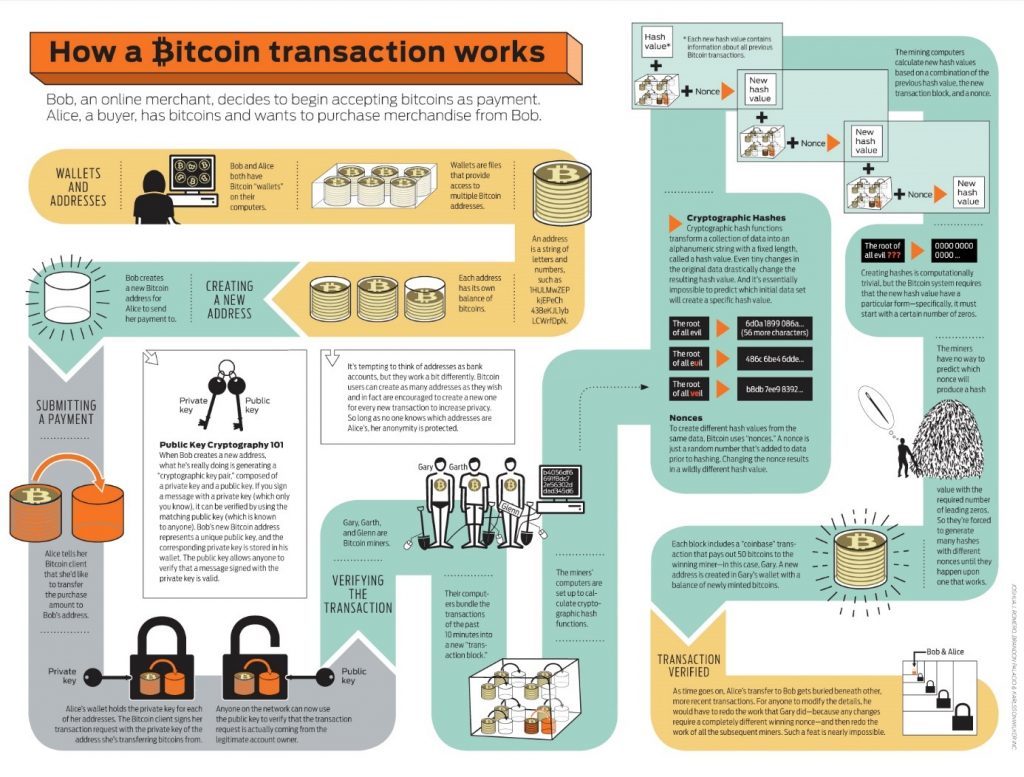
Here is an excellent visualization of how Bitcoin transactions work. Compliments to the website where I got it from: http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2013-05-12/visualizing-how-bitcoin-transaction-works
The rise of blockchain currencies
New currencies have been developed to enable transactions. The more well-known currencies that are currently available are Bitcoin and Ethereum. Let’s focus on Bitcoin. Bitcoin has its own blockchain where Bitcoin is the currency. Because a limited amount of additional Bitcoin becomes available, any additional demand for Bitcoin increases the price due to simple economy of supply and demand. If demand increases and supply stays the same, the price increases[v]. The value of 1 bitcoin has increased from $443 at the beginning of 2016 to over $5000[vi] today (15-10-2017) because of this[vii].
But why do parties want to use cryptocurrencies and in particular Bitcoin to make transactions? Its value is based on demand only and there is already a global network to make fast payments from one party to another created by banks. A big advantage of blockchain transactions over banking transactions is that they cut out the middleman. In order to establish a transaction that is acceptable to all parties involved, there needs to be a degree of trust that the transaction will happen in the way that was agreed. At this moment, two parties are only able to conduct transactions because they trust a third party, in most cases a bank, to make sure everything goes smoothly. In exchange for this service, a lot of personal information has to be given to the bank so that they can make this transaction possible. Transactions on a blockchain don’t need this exchange of private information with a third party. All transactions are recorded and traceable by everybody, and due to the way blockchain works, it is impossible to make a false payment. The only way to reverse or change a transaction is with a new transaction, both of which will appear on the blockchain. Also transactions happen fast. Compared to money-wiring companies, bitcoin transactions surely has the edge[viii]. Furthermore, blockchain payments can be made anonymously, only allowing others to see the code of one’s cryptocurrency address, giving up no further personal information whatsoever[ix].
Also, eliminating the need for a third-party makes transactions more cost-effective, and opens up transactions to all the people that don’t have access to banks, which is estimated to be around half of the global population[x].
The future
At this point in time, blockchain is mainly used to facilitate payment systems that have some advantages over more traditional systems. All in all this doesn’t change the world as we know it. However, blockchain technology opens up so many more possibilities that will not only revolutionize business but will shake up some things like how we vote for a new government and the way intellectual property works. Besides that, it will give us back a lot of privacy and prevent fraud, give global access to safe and efficient payment systems, provide an enormous new platform for business, take power from large organizations and give it back to the public and make cybersecurity that much easier. Due to the vast disruptive power of blockchain, a complete visualization of the ‘new world’ is impossible and would take more than a student’s attention span to portray[xi]. Therefore I chose two blockchain initiatives that illustrate how blockchain can stir up our world. At this moment, cyber security is more important than ever. Meaningful websites occasionally get attacked by so called DDOS attacks which are quite hard to defend. A DDOS attack is basically an attempt to create so much web-traffic to one website that it can no longer handle the pressure and shuts itself down. A blockchain startup now wants to create a blockchain based network that pools the computing-power of all participants and uses this to properly defend against such attacks. The moment one website gets attacked, all the spare computing power of the other participants is pooled and absorbs the attack. When computing power is contributed, a party is rewarded with money. This way, all parties are protected extremely cost-effectively. Another example of how blockchain will help change the world is the way intellectual property and its rewards work. Say you are a musician that works hard to get round. Having your property, your music, downloaded daily without getting any reward is frustrating. Putting your music on a blockchain makes it impossible to download without anyone finding out, and the ownership of your music will always be traceable back to you. This makes it a lot harder to download, copy and modify music for others without somehow rewarding you. Because cryptocurrency is divisibly in such extremely small amounts[xii], immediate payments for e.g. listening to your sweet new techno track can be rewarded from user to producer in a micro-transaction. This is just a tiny grasp of some lesser impactful initiatives that are already ongoing. Changes in society are due, and you can be a part of this, or at least understand what is going on. Reading this article might be your first step, but I encourage everybody to take it further[xiii].
________________________________________________________________________________________________
[i] Currency used on blockchains is coded in a way that each piece of currency has a unique code, much like serial numbers on cash. For Bitcoin in particular, it is coded in a way that 1 Bitcoin is dividable into 10^8 small uniquely identifiable pieces called Satoshis
[ii] Open these links for clear explanations of how the money creation process works, both for banks and central banks http://positivemoney.org/how-money-works/how-banks-create-money/ http://positivemoney.org/how-money-works/advanced/how-central-banks-create-money/
[iii] Other cryptocurrencies use other reward-systems than Bitcoin. What decent reward structures all have in common is that all parties agree the reward-structure is fair and there is no way to cheat into obtaining easy cryptocurrency. Also, the reward structure should keep the blockchain decentralized and not put all the power in one or in a few people’s hands.
[iv] Mining Bitcoin has grown to be a competitive activity on its own. Computing power costs energy and an initial investment. If the number of parties that mine Bitcoin grows, the reward for each party on average decreases. If Bitcoin rises in value, the average reward of Bitcoin is worth more in e.g. Dollars. At this point the market is competitive enough that letting your laptop mine Bitcoin will only cost you money. Only Mining-farms are able to make money on this market at the moment. Do note: Bitcoin is already making plans to change the reward system in the future to decentralize Bitcoin even more.
[v] Despite its digital nature, it is possible to lose a bitcoin like it is possible to lose a 5 euro note. Bitcoins can be downloaded onto external hard-drives, which can be lost. This makes bitcoin an even more intrinsically deflating currency. Personally I get a good laugh at the situation where someone somewhere probably lost a hard-drive with e.g. 10 bitcoins on it from the time they were valued at around €3,0, which would now be worth €40.000
[vi] In the process of writing this article, I had to change this number from 4000 to 5000.
[vii] Besides the amount of users that want to use Bitcoin to make trades, the rapidly expanding market and price of Bitcoin also attracts investors that buy Bitcoin to profit from its value increase. This has two price-driving effects. The first is that new investors cause new demand for the currency. This drives up the price, because supply doesn’t increase. Also, any party that buys and holds an amount of Bitcoin takes this amount of coins away from the active market, leaving less total Bitcoins available to make transactions for more active parties. This drives up the price even further.
[viii] This is especially appealing to foreign workers. E.g. a Mexican working in America that wants to send home a part of his earnings has to pay high fees to money-wiring companies, which also take a long time to transfer the money.
[ix] A cryptocurrency address is basically a string of letters and numbers that functions as a personal wallet. There is no direct way to link a person to such an address, making anonymous transactions possible. The possibility of anonymous payment has a special appeal to those in the criminal sector. This is one of the reasons Bitcoin was able to grow so quickly. Illegal criminal marketplaces like Silk Road operate with Bitcoins, making it extremely hard to trace criminal money. This is one of the unwanted effects blockchain inevitably brings.
[x] This statistic comes from the book ‘Blockchain for dummies’, online available through this link: https://www-01.ibm.com/common/ssi/cgi-bin/ssialias?htmlfid=XIM12354USEN (page 5)
[xi]To actually get an idea of the changes blockchain might bring to society, I greatly recommend the book: Blockchain Revolution’, available here (not sponsored. Genuine advice): https://www.bol.com/nl/p/blockchain-revolution/9200000052361215/?suggestionType=typedsearch ,
[xii] To illustrate: A bitcoin is divisible in 10^8 pieces. At the moment a bitcoin is worth around €4000, so a payment as small as €0.00004 can be made. This can also definitely be made even smaller in the future.
[xiii] Eager to learn more about blockchain? Here are some links that can get you started. https://www-01.ibm.com/common/ssi/cgi-bin/ssialias?htmlfid=XIM12354USEN, https://www.ted.com/talks/don_tapscott_how_the_blockchain_is_changing_money_and_business/transcript
And a link for the investors that like to dream: https://www.cnbc.com/2017/05/31/bitcoin-price-forecast-hit-100000-in-10-years.html